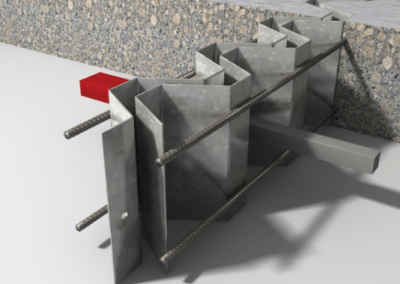
Jointing Systems
CORKJOINT® is a specialist in the development, manufacture and supply of Jointing Systems
In construction projects, control, contraction and expansion joints are used to control and manage the stresses and movements that occur within a structure due to environmental conditions such as temperature changes, moisture variations, and settling. These joints are designed to allow for movement and expansion, prevent cracking and buckling, and maintain the structural integrity of the building.
CORKJOINT® has a number of different types of Jointing Systems available for use and all have been designed for very specific types of applications and requirements.
CORKJOINT®’s Jointing Systems have been designed to help fast-track the construction process and some are as basic as inducing cracks in concrete to form a control joint or as heavy duty as a structural connection for use in transferring high shear loads across movement joints.
Click on the images below to view the product details. If you can’t find what you’re looking for on our website, ask, and we will source it for you.
Control Joints
Control joints are designed to control the location and distribution of cracking in concrete structures. They are typically installed in predetermined locations, such as at regular intervals, at changes in plane or direction, or at points of concentrated loads. The purpose of control joints is to divide the concrete into smaller, manageable sections, which will crack in a controlled manner when subjected to movement or expansion.
Control joints can be formed in a variety of ways, including saw cuts, formed grooves, and pre-molded joint strips. They may be filled with a flexible joint filler material, such as silicone or polyurethane, which allows for movement and expansion while maintaining the joint’s seal.
In addition to controlling cracking, control joints also provide aesthetic benefits by creating clean, straight lines in the concrete surface. They also help to reduce maintenance costs by minimizing the need for repairs due to uncontrolled cracking.
Contraction Joints
Contraction joints, also known as isolation joints, are designed to create a gap between concrete elements, such as slabs or walls, to allow for movement and contraction due to temperature changes or moisture variations. The purpose of contraction joints is to prevent cracking and buckling in the concrete structure by allowing for controlled movement and expansion.
Contraction joints are typically installed at regular intervals, often at intervals of 20 to 30 feet, depending on the climate and environmental conditions of the area. They can be formed using pre-molded joint strips, metal or plastic joint materials, or by creating a gap between the concrete elements.
Unlike control joints, contraction joints are left unfilled, allowing for free movement and expansion. This also prevents the buildup of pressure that can occur when joint filler materials are used in control joints.
Contraction joints are essential to the longevity and durability of concrete structures. Without contraction joints, concrete can buckle, crack, and become damaged due to uncontrolled movement and expansion.
Expansion Joints
Expansion joints, also known as movement joints, are used in construction to accommodate the natural movement and thermal expansion and contraction of building materials. Their primary function is to provide flexibility and prevent damage caused by the expansion and contraction of various components due to temperature changes, moisture, seismic activity, or other factors. Expansion joints play a crucial role in ensuring the longevity, safety, and functionality of buildings by accommodating movement and preventing damage that could result from the natural forces and environmental conditions that affect construction materials.
Joint Maintenance
To ensure that control and contraction joints continue to function properly, regular maintenance is required. This includes inspecting the joints for damage or deterioration, cleaning the joints of debris and excess filler material, and resealing or refilling the joints as needed.
If joints are not properly maintained, they can become clogged with debris or filler material, which can prevent them from allowing for movement and expansion. This can lead to cracking, buckling, and other damage to the concrete structure.
In conclusion, control, contraction and expansion joints play an essential role in the durability and longevity of concrete structures. By allowing for controlled movement and expansion, these joints help to prevent cracking, buckling, and other damage that can occur due to environmental conditions. Proper installation and maintenance of control, contraction and expansion joints is essential to ensure their continued functionality and effectiveness.